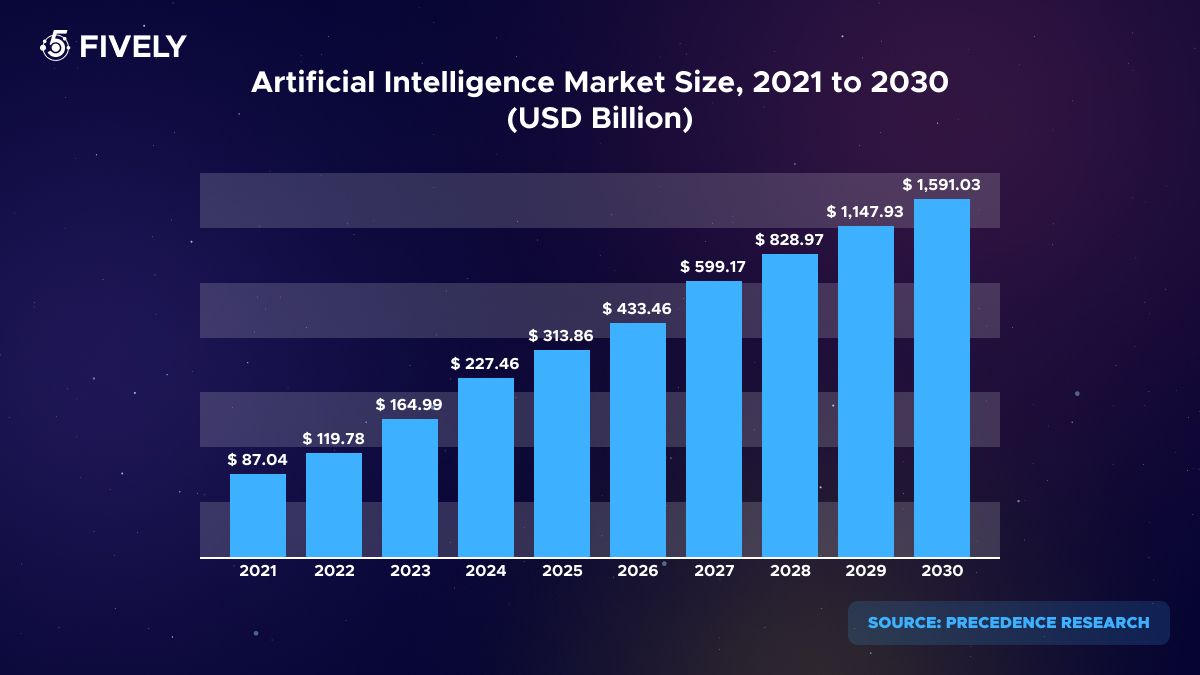
Artificial Intelligence: A Potential Threat or Solution for the Sustainable Environment?
Join us as we examine the dichotomy of AI's potential as both a threat and a solution for a sustainable future.
AI is indeed enhancing the quality of life, but at what cost? MIT researchers found out that the CO2 emissions generated from training intelligent AI models can be a staggering 5 times greater than those produced by an average American car throughout its entire lifespan, including manufacturing.

But does it mean that we should abandon AI with all its benefits and return to the tediousness of manual work? Absolutely not! The right strategy enables AI to make a U-turn and tip the scales in the global ecology fight in the green’s favor.
Let’s find out how AI can help address ecological challenges!
What Is Sustainable AI In Simple Terms?
Sustainable AI (or green AI) is an eco-friendly approach to Artificial Intelligence systems that aims to minimize their hazardous impact on the environment. In the same way that Microsoft is using renewable energy sources for its cloud data centers, businesses around the world strive to optimize every step of AI leveraging to leave a smaller carbon footprint on the planet and produce fewer pollutants.
Green AI is also about using its power for different activities and programs for preserving ecology and combating climate change. For example, AI-driven tools can forecast natural disasters or detect patterns in sea levels by analyzing data from drones, satellites, and IoT devices.
Why AI Must Become More Sustainable to Ensure a Safe and Green Future
AI is not an inherently damaging technology, and its impact is determined by how it’s used. Here are just 3 aspects that directly affect the environment:
1. Energy consumption
The IT industry’s global consumption of electricity is predicted to stand at 8–21% by 2030. Even before AI starts to work, it demands a lot of energy and worsens the energy crisis, which started in the aftermath of COVID-19.
Then, for AI programs to be effective, they require huge amounts of data to be processed, analyzed, and stored. All these involve a lot of computational power, hence energy.
The research shows that the largest data centers in the world need 100 megawatts of power capacity, which is enough to power around 80,000 households in the US. By the way, these huge data centers need energy not only on processing data itself but, for example, for cooling the hardware, which, along with servers, accounts for the highest energy consumption.
The problem here is not so much the amount of energy as where it comes from. Even today, much of the power derives from fossil fuels or other non-renewable sources. Data centers within the ICT industry are responsible for 45% of the carbon footprint, and it goes without saying that this has a significant impact on climate change.
However, custom AI solutions can optimize energy consumption in various sectors, including smart grids, buildings, and industrial processes. By reducing energy waste, it indirectly helps mitigate ecological impacts related to energy production
2. e-Waste.
It’s rather difficult and expensive to safely dispose of byproducts, residues, or materials discarded during the manufacturing of AI hardware. An average of 58 Million Metric Tons (Mt) of e-waste is produced annually, and only 17.5% is properly recycled. This amount is extremely small, considering that it contains lead, cadmium, and other materials that can deteriorate nature, while aluminum and copper produce harmful chemicals when burned.
3. Water consumption
Do you know how much water is used by a small town with a population of ten to fifty thousand people? From 1 million to 5 million gallons. The same amount is consumed by one large data center. They’re often located in places where water resources are already scarce, and they continue to be exhausted to cool servers.
The last point is connected to every aspect above. The manufacturing of AI hardware involves the production of silicon chips that often serve for memory storage. Their manufacturing process doesn’t only pollute the environment with hazardous waste but also requires a lot of water and electricity. And, well, it’s predicted that soon the need for silicon will outpace its actual production due to the current levels of data generation, so the unstoppable circle of manufacturing and polluting repeats itself over and over again.
But the picture is not as dire as it might seem. We need to accept some trade-offs, especially when the technology is promising to benefit the environment when in safe hands.
What is the European Green Deal?
The EU set an objective to become the first climate-neutral continent with a circular economy by 2050, and the European Green Deal was launched to achieve it. The overall funding amount is €1 trillion. This enables management to invest in innovative projects that would move the strategy forward towards its goals, not only on the local level but also globally.
The EU Green Deal concerns, in effect, every aspect whose advancement would contribute to making the environment cleaner. Some of them are:
- Clean energy;
- Sustainable industry;
- Eliminating pollution;
- Research and development;
and others.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Advancing the European Green Deal
Even though this technology has played a role in the deterioration of ecology, AI and sustainability are becoming best friends, driving the transformative potential of the European Green Deal.
What is the main benefit of AI? Its ability to process heaps of data and make precise predictions. Not only are these virtues of AI advantageous to businesses, but to almost every aspect set forth by the Green Deal. All its subsets, alone or in combination with other technologies like IoT and cloud computing, can make a significant difference in creating an unpolluted environment.
Here are just some of the examples of how AI is used to preserve the environment.
AI and Carbon Footprint
AI models can present businesses with an accurate estimate of their carbon footprint by assessing various parameters such as their region, cloud provider, and type of equipment they use. The insights received enable businesses to render data-driven decisions on the optimization of their resources or migration to another cloud.

AI and Power Consumption
AI algorithms can analyze real-time data from smart meters, sensors, and other IoT devices to optimize energy consumption in homes and industrial facilities. For instance, AI can advise on the efficient use of heating, cooling, and lighting based on usage patterns.
Individuals may have AI integrated into smart devices and manage the power modes of smartphones, laptops, and other gadgets to extend battery life and reduce overall energy consumption.
Businesses can apply the same tools, but in scaled versions. Here, AI can optimize power grids by predicting energy demand and managing energy storage systems to ultimately balance the supply and demand of electricity.
AI and Deforestation
The most recent example of an AI that helps prevent Amazon deforestation is PrevisIA. Researchers were concerned that similar tools can only make long-term predictions about complete deforestation, while real action is needed at the moment. Eventually, they've come up with a smart algorithm that analyzes satellite images and provides annual predictions for forest depletion.
It takes into account not only the images of forests themselves but other factors contributing to the deterioration. So, today, the tool maps the construction of illegal roads and logging sites and alerts the authorities about possible deforestation areas. The precision is high: 85% of alerts happened within 4 km of the predicted area.

AI and Agriculture
Here, it might also minimize water leakage for agriculture is responsible for an average of 70% of all freshwater withdrawals in the world. A more sustainable approach to water and crop management may be worked out by AI’s analysis of climate, temperature, and humidity levels. Farmers can finally make decisions based on real data, reducing waste, choosing the right pesticides, and automating lots of agricultural activities.
Take combine operations, for example. Before, human workers had to adjust the sieve themselves, while now special sensors can differentiate good-quality grain from foreign materials and alter the sieve mode automatically.
AI and Water Management
In Australia, AI coordinates water pump movements to reduce the amount of electricity wasted. It derives historical data on daily water use and automatically sends instructions to the pump system. The system proved its efficiency at Melbourne’s biggest treatment plant, where energy costs were reduced by 20%.
Did you know that faulty pipes caused the leakage of about 2.9 million liters of water a day between 2021 and 2022 in England and Wales? AI platforms also allow for reducing water wastage by detecting burst pipes and analyzing equipment anomalies to take preventive measures or stop the leakage as soon as possible.
AI for Buildings and Construction
As you might already infer, AI in the sustainability of buildings boils down to cutting energy consumption through various sensors that monitor optimal temperature and occupancy. Such tools can also gain insights from the outside weather and adjust air conditioning and heating systems accordingly.
As for construction, AI-driven autonomous machinery is used to reduce fuel consumption by optimizing routes, avoiding unnecessary movement, and coordinating tasks effectively. What’s more, they can analyze environmental conditions on construction sites to ensure compliance with regulations and minimize negative effects on the surrounding ecosystem.
Or, another way to leverage AI, is to let it perform life cycle assessments of buildings to evaluate their environmental impact from construction to demolition. They may as well suggest materials that are better suited for the specific building by analyzing their ecological footprint throughout raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, and disposal.
Conclusion
AWS started their switch from diesel to hydrotreated vegetable oil for creating chips for their data centers, claiming it’ll ultimately diminish their emissions of greenhouse gasses. The whole world is moving towards sustainability and environmentally friendly ways to conduct their businesses as the amount of data processed by every client-oriented company today is enormous, and it’ll only continue to increase.

Today, we have a choice: to plan long-term and use AI to preserve natural resources, or to seek momentary profit and then suffer from the consequences of global climate change. Of those consequences, we’re informed and fully aware, which makes the perpetuation of the ecological crisis far from inadvertent. In just a decade, this choice won’t matter when the deterioration of our habitat becomes irreversible.
So, let’s just keep in mind that even a minor change in the way we organize our workflow and utilize resources can relieve the planet from unnecessary strain, and AI is always here to help us in this noble endeavor.

Need Help With A Project?
Drop us a line, let’s arrange a discussion