AI Prompts for Code Review Every Developer Should Use in 2026
A practical guide to the most powerful AI prompts for code review in 2026, helping developers detect bugs, improve architecture, strengthen security, and ship faster.
Code reviews are one of the most critical stages of the development lifecycle: they shape code quality, architecture clarity, performance, scalability, and even long-term maintenance costs. But manual reviews alone can be slow, inconsistent, and heavily dependent on the reviewer’s experience. This is where AI prompts for code review come in: with the right instructions, ChatGPT and other AI models can analyze your code, surface hidden issues, suggest improvements, and act as a senior reviewer at scale.

In this article, we’ll explore the most effective prompts used by engineering teams to review code architecture, detect vulnerabilities, eliminate anti-patterns, and ensure your codebase is clean, secure, and built for the future.
Why AI Code Review Is Important
The first reason is that codebases today are larger, more complex, and more interconnected than ever, and development moves faster than traditional review cycles can handle. AI brings an extra set of trained eyes that can analyze patterns, highlight risks, and detect issues in seconds.
Also, AI code review helps teams maintain architectural integrity, enforce consistent coding standards, and eliminate subtle bugs before they reach production. It identifies missing tests, potential security flaws, performance bottlenecks, and duplicated logic, all optimized with best-practice alternatives. With AI prompts guiding the review, engineers can uncover problems earlier, spend less time on low-value checks, and focus more on long-term decisions, system scalability, and crafting better solutions.
In short: AI code review increases code quality, shortens review cycles, reduces technical debt, and helps teams ship faster with confidence.
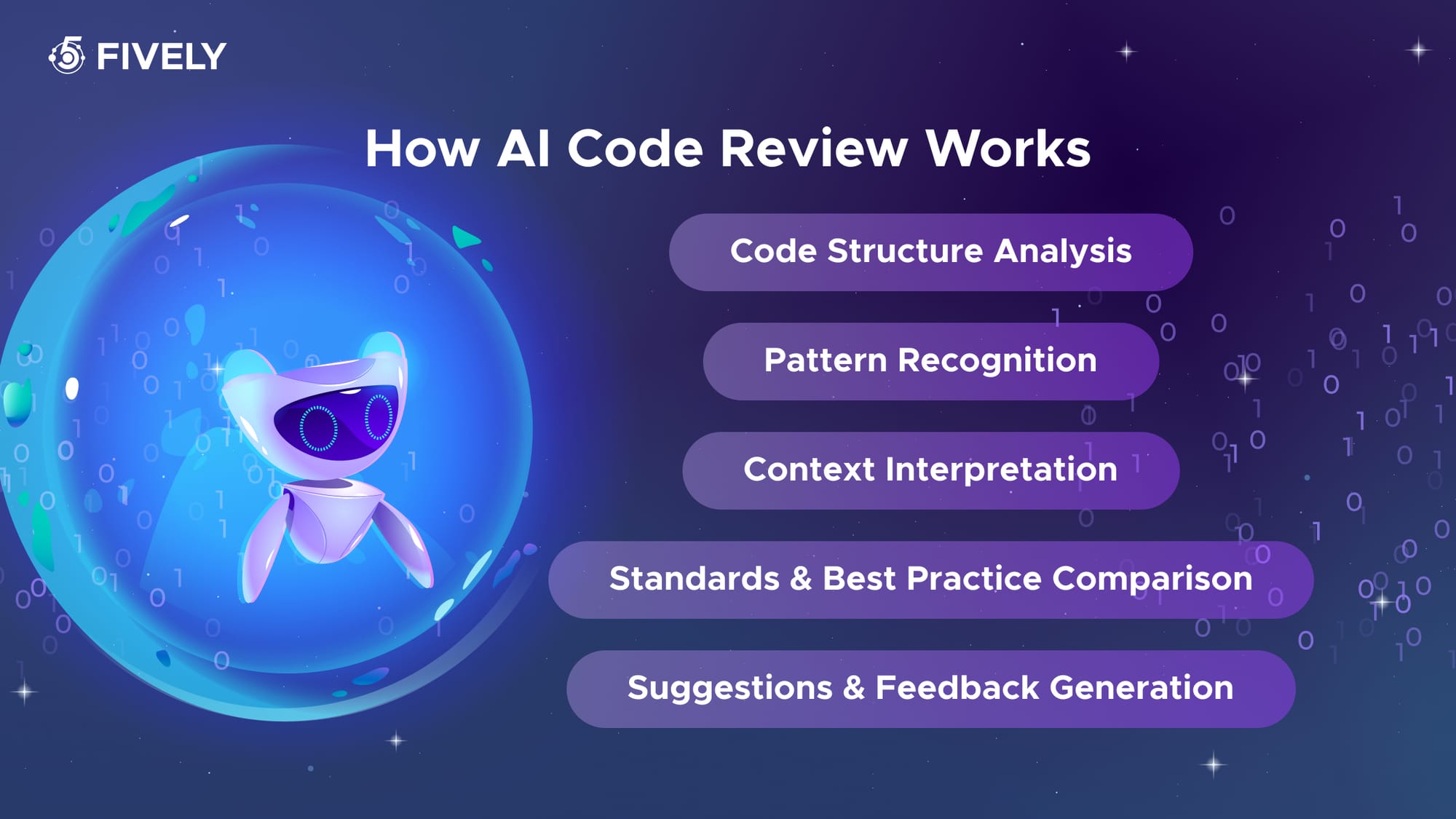
How AI Code Review Works
AI-driven code review relies on a mix of pattern detection, structural analysis, and learned engineering principles. Instead of manually scanning files, developers provide a code snippet or repository context, along with clear instructions on what to analyze. From there, the model examines the code at multiple levels to surface potential issues and recommend improvements.
Here’s the typical workflow behind an AI-assisted code review:
1. Code Structure Analysis
The model breaks down the submitted code, reading its syntax, logic flow, function organization, and naming conventions.
2. Pattern Recognition
LLM detects common coding patterns — as well as anti-patterns — learned from large volumes of industry examples, open-source projects, and best-practice repositories.
3. Context Interpretation
The AI evaluates how the code interacts with surrounding components, business logic, dependencies, and frameworks to understand the intended outcome.
4. Standards & Best Practice Comparison
It cross-references the implementation against recommended patterns, architecture principles, secure coding standards, and performance guidelines.
5. Suggestions & Feedback Generation
Finally, the model produces structured feedback: highlighting risks, inconsistencies, inefficiencies, unclear logic, missing tests, or unsafe implementations, while offering actionable improvements.
What influences the quality of AI code review?
- Prompt clarity – The more precise the request, the more accurate the evaluation
- AI-powered Model knowledge base – Its exposure to reliable coding standards and modern frameworks
- Domain complexity – Niche architectures, low-level optimizations, or highly specialized logic may require expert oversight
- Business context – AI still struggles to fully understand internal rules, edge cases, and product-specific constraints without explicit context
When used correctly, AI review becomes an invaluable assistant — fast, consistent, and able to analyze code at scale. Human engineers still make final decisions, but AI significantly reduces oversights, speeds up review cycles, and offloads tedious checks so teams can focus on architecture, product vision, and long-term technical health.

General Code Review Prompts
Prompt 1:
Review this Python code for readability, maintainability, and structural quality. Identify unclear logic, unnecessary complexity, duplication in code, missing comments, and violations of common best practices. Provide specific improvement suggestions.
Prompt 2:
Analyze this React code as a senior engineer. Point out potential issues, performance problems, questionable decisions, and any architectural concerns. Offer concrete fixes or refactoring steps.
Prompt 3:
Examine this C# code and list all risks you see: security, logic mistakes, edge cases, scalability limitations, and dependency issues. Add recommendations for each.
Style & Best Practices
Prompt 1:
Check this piece of code against common coding standards, design patterns, naming, formatting, structure, DRY, SOLID. Highlight anything that doesn’t follow clean-code principles and propose corrected examples.
Prompt 2:
Identify any anti-patterns, unclear variable names, nested logic, or over-complicated conditionals. Suggest cleaner alternatives that improve readability.
Prompt 3:
Evaluate whether this code follows best practices for the framework or language used. If something is outdated or stylistically weak, propose modern, idiomatic replacements.
Error Handling Suggestions
Prompt 1:
Review this Node.js code for potential edge-case failures. Identify missing null/undefined checks, unhandled exceptions, unsafe assumptions, and missing error returns. Suggest safe handling approaches.
Prompt 2:
Check whether this Rust code gracefully handles API/network errors, timeouts, and invalid responses. If not, recommend and show better defensive error handling.
Prompt 3:
Analyze exception handling strategy in this snippet. If error handling is too vague, missing, duplicated, or silent — highlight it and suggest clean patterns to implement instead.
Code Quality Analysis
Prompt 1:
Score this .net code from 1 to 10 based on clarity, maintainability, testability, performance, and architecture. Explain the score in bullet points and show key fixes that would raise it.
Prompt 2:
Break down the biggest sources of technical debt in this code snippet. Rank them from highest to lowest impact and propose refactoring steps for each.
Prompt 3:
Check for unnecessary complexity, large functions, repeated logic, overly large classes, or mixed responsibilities. Recommend how to simplify structure and improve cohesion.
Simple Critical Issue Review
Prompt 1:
Scan this Rect code for critical problems only: security risks, potential data leaks, race conditions, SQL injection, unsafe cryptography, or thread-safety issues. List only high-severity items and how to fix them.
Prompt 2:
Pretend you are performing a final pre-release audit. Identify anything that could break in production, cause performance degradation, or crash under load. Provide exact fixes, not just descriptions.
Prompt 3:
Check this Java code for anything that can produce runtime exceptions, undefined behavior, or unexpected side effects. Make recommendations with corrected code blocks.
Debug Prompts for Faster Issue Resolution
When something breaks, behaves strangely, or produces unclear error logs, AI can quickly isolate the problem, explain root causes, and propose working fixes. Below are prompts tailored specifically for debugging scenarios.
Error Message Debugging
Prompt 1:
Here is an error message and the code that triggered it. Identify the root cause, explain what is happening under the hood, and propose step-by-step fixes with updated code.
ERROR:
{paste logs}
CODE:
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Analyze this stack trace and explain the exact origin of the error, what function is failing, and why. Suggest the minimal code changes needed to resolve it safely.
Prompt 3:
Based on this error message, list the three most likely causes, rank them by probability, and show how to confirm each. Include code examples where relevant.
Unexpected Behavior Analysis
Prompt 1:
This code produces incorrect or unexpected output. Identify logical mistakes, hidden assumptions, or missing conditions. Explain the root issue and provide corrected code.
{paste code or behavior description}
Prompt 2:
Compare the intended behavior with the actual result and tell me where the code deviates. Highlight flawed conditions, state handling, or incorrect calculations.
Prompt 3:
Walk through the execution path of this function line-by-line, explain what the program is doing at each step, and pinpoint where execution diverges from intended logic.
Script Debugging with Fix Suggestions
Prompt 1:
Find bugs, runtime traps, incorrect assumptions, or anti-patterns in this script. Rewrite only the affected parts with corrected logic and clearer structure.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Perform a deep debug scan: missing variable checks, unhandled return values, uninitialized states, incorrect async usage, leaking resources, blocked promises, and performance bottlenecks. Provide fixes for each issue you flag.
Prompt 3:
Debug this code with a focus on data flow: highlight misuse of props, state, parameters, mutable data, or stale values. Recommend safe and clean changes to guarantee predictable results.
Error-Handling Mechanism Review
Prompt 1:
Review how errors are handled in this snippet. Identify weak or missing error states, silent failures, overly broad catch blocks, or bad logging. Suggest proper error handling patterns with examples.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Check if this code correctly handles edge cases (timeouts, invalid inputs, empty responses, and failed API calls). Propose stronger error paths and add defensive checks where needed.
Prompt 3:
Evaluate this code for resilience: where can it throw, break, misinterpret data, or lose state? List vulnerabilities and show how to strengthen reliability with clearer safeguards.
Issue Detection Prompts
AI can help you uncover bugs before they reach production by scanning code for hidden logic flaws, edge-case vulnerabilities, incorrect assumptions, and faulty recursion logic. These prompts help detect issues early and guide corrective improvements.
Potential Bug Identification
Prompt 1:
Scan this code for potential bugs, fragile logic, unhandled data states, or incorrect assumptions. List each issue with a short explanation and suggest a corrected version.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Identify any bug-prone parts of this code: null handling, type mismatches, undefined behavior, async misuse, incorrect loops, or risky conditions. Show safer alternatives.
Prompt 3:
Check for hidden defects that may not throw errors immediately but could break under real-world scenarios: concurrency issues, timing problems, stale data, or race conditions. Explain how to reproduce them and fix them.
Logic Error Detection
Prompt 1:
Review this code for logic mistakes: incorrect condition checks, inverted comparisons, flawed branching, wrong data flow, or missing return paths. Explain what’s wrong and provide corrected logic.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
List where logical assumptions fail in this implementation. Highlight oversights such as values not checked, edge cases not considered, or incorrect boundaries.
Prompt 3:
Walk through this code step-by-step and tell me exactly where the logic becomes inconsistent with the intended outcome. Provide a corrected flow.
Function Error Spotting
Prompt 1:
Analyze this function for problems with scope, parameters, missing input validation, inconsistent returns, side effects, or incorrect argument usage. Suggest improvements with fixed code examples.
{paste function}
Prompt 2:
Check if this function violates clean code principles: too many responsibilities, inconsistent naming, hidden dependencies, or complex branching. Recommend a cleaner and safer structure.
Prompt 3:
Point out any unused variables, redundant expressions, unreachable code, or missing guard clauses inside this function. Rewrite only the parts that require correction.
Recursive Function Issues
Prompt 1:
Review this recursive function for infinite-loop risks, missing base cases, incorrect recursion depth, or stack overflow potential. Suggest safer recursion or iterative alternatives.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Check whether each recursion call moves the state closer to termination. Identify any logic that could cause repeated looping, excessive memory usage, or unnecessary branching.
Prompt 3:
Analyze this recursive logic for performance concerns: duplicated calculations, input-size complexity, or exponential branching. Recommend memoization or iterative solutions where helpful.
Performance Review Prompts
Clean code isn’t enough — it must also run fast, scale well, and conserve resources. These prompts help AI uncover hidden performance issues, memory leaks, scalability risks, and execution bottlenecks before they become production failures.
Performance Issue Identification
Prompt 1:
Review this code for potential performance issues: expensive operations, inefficient loops, heavy computations, redundant calls, or unoptimized logic. Suggest faster alternatives with examples.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Identify any slow patterns, repeated work, blocking operations, or poor handling of async tasks that may negatively affect response time or throughput. Recommend optimizations.
Prompt 3:
Evaluate this code for performance under high load. Point out anything that might degrade speed when scaling: data structures, I/O frequency, or algorithmic complexity. Offer improvements.
Memory Leak Detection
Prompt 1:
Scan this code for potential memory leaks, unresolved references, non-cleared timers, unused objects, or excessive data retention. Explain the risks and show corrected patterns.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Detect variables, listeners, closures, or DOM nodes that may stay in memory longer than needed. Suggest cleanup strategies (like disposal, unmount logic, or lifecycle fixes).
Prompt 3:
Check this code for inefficient memory usage: large buffers, unnecessary caching, or unbounded arrays. Provide safer memory–conscious alternatives.
Scalability Analysis
Prompt 1:
Analyze this implementation for scalability risks. Identify areas that may fail under volume: heavy synchronous tasks, deep nesting, single-thread choke points, or data structures that don’t scale. Recommend scalable patterns.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Check if this architecture can handle thousands of concurrent users or large datasets. Highlight weak points — locking issues, message queues, caching strategies, database calls — and propose improvements.
Prompt 3:
Assess whether this solution can scale horizontally or vertically. If not, explain why and suggest architectural changes that enable growth.
Bottleneck Identification
Prompt 1:
Identify execution bottlenecks in this code: nested loops, blocking I/O, expensive DB calls, serialization overhead, or repeated computations. Recommend precise fixes.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Locate any part of the code that could restrict performance in production: rate limits, queue depth, CPU-bound logic, or missing caching. Provide optimization strategies.
Prompt 3:
Perform a complexity analysis, estimate time/space costs, and point out bottlenecks with the highest impact. Suggest refactors that reduce complexity and improve throughput.
Security Review Prompts
Security should never be an afterthought. These prompts help AI uncover risky implementations, unsafe data handling, injection vulnerabilities, authentication gaps, and logic flaws before they reach production.
Vulnerability Detection
Prompt 1:
Review this code for security vulnerabilities, insecure logic, weak access control, unsafe data handling, missing validations, and risky external calls. List all issues with explanations and propose fixes.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Evaluate this implementation against OWASP Top 10 risk categories. Identify anything that could lead to data leaks, privilege escalation, injection attacks, or denial of service. Suggest hardened patterns.
Prompt 3:
Check if this code exposes sensitive information: tokens, credentials, internal paths, or stack details. If so, suggest masking, encryption, or safer handling.
SQL Injection Checks
Prompt 1:
Analyze this database query logic for SQL injection risks. Detect unsafe concatenation, unvalidated user input, malformed queries, or missing parameter binding. Provide secure code alternatives.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Check all query-building patterns here. If any user input touches the database without sanitization, highlight it and rewrite the query using prepared statements, ORM filters, or parameterized queries.
Prompt 3:
Review this backend code and map all input paths that reach the DB layer. Flag any route that allows direct or indirect SQL injection attempts, and recommend stronger validation and escaping.
XSS Vulnerability Analysis
Prompt 1:
Scan this code for XSS risks: unsafe DOM rendering, unescaped variables, dynamic HTML, or direct insertion of user data into UI. Suggest safe sanitization methods.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Check whether user-generated data is displayed without encoding or sanitization. If so, identify the risk level and show secure rendering patterns.
Prompt 3:
Analyze this frontend/backend flow for potential stored or reflected XSS. Point out any injection vectors, suspicious endpoints, or missing sanitization.
Authentication Flaw Identification
Prompt 1:
Check the authentication and authorization logic in this code. Identify incorrect permission checks, insecure token handling, missing role validations, or weak login mechanisms. Suggest mitigation.
{paste code}
Prompt 2:
Analyze how JWTs, sessions, or cookies are stored and validated. If lifetime, signing, rotation, or refresh logic is unsafe, highlight weaknesses and advise secure patterns.
Prompt 3:
Inspect this code for authentication bypass risks: trust in client-side flags, missing server-side validation, predictable tokens, or reuse of cached credentials. Propose hardened logic.
Benefits of AI Tools for Coding Review
Teams can leverage AI-assisted code review to bring structure, speed, and accuracy to one of the most critical stages of software development. Instead of relying solely on manual effort, teams gain an intelligent layer of analysis that identifies issues earlier, reduces review time, and improves overall engineering quality.
Here are the core benefits:
Faster and More Consistent Reviews
AI evaluates code in seconds, flagging structural issues, bugs, and stylistic inconsistencies without fatigue or oversight. It delivers consistent review standards across the entire team, regardless of contributor experience.
Reduced Technical Debt
By surfacing weak design choices, duplicated logic, and hidden architectural flaws early, AI helps prevent long-term maintenance headaches and lowers the cost of refactoring.
Stronger Security Checks
LLMs can detect insecure patterns, missing validations, potential injection vectors, or unsafe authentication logic that might be overlooked in a fast-paced manual review.
Higher Development Velocity
Engineers spend less time on repetitive review cycles and more time on building features. Faster approvals, fewer revision rounds, and cleaner pull requests accelerate the entire delivery pipeline.
Improved Code Quality and Standards
AI enforces formatting norms, best practices, test expectations, and framework-specific patterns — helping teams maintain a unified code style no matter how large they scale.
Support for All Seniority Levels
Junior and mid-level engineers get instant code guidance, while senior reviewers can focus on architectural or system-level reasoning instead of formatting, naming, or minor refactors.
Cost-Effective Review Process
Fewer review loops, faster risk detection, and reduced post-release bug fixing lead to shorter timelines and lower engineering costs.
Best Practices for AI Code Review and Debugging
AI can significantly improve code quality — but only when it’s used intentionally. Treat it as a powerful assistant, not a replacement for sound engineering judgment. The practices below ensure your AI review sessions are accurate, actionable, and aligned with your team’s standards.

Use Clear, Structured Prompts
Ambiguous prompts lead to vague feedback. Be specific about what you want reviewed (architecture, logic, errors, security risks, performance issues, etc.).
Define the depth of review, expected output format, and improvement suggestions.
Always Provide Context
AI shouldn’t have to guess how the code fits into your system. More context = better feedback. Include in your prompt:
- file purpose
- inputs/outputs
- surrounding components
- business logic
- constraints or performance goals
Pair AI Review With Human Validation
AI flags issues fast, but humans evaluate trade-offs, architecture direction, product constraints, domain edge cases, and real-world impact.
Use AI as the first scan, not the final authority.
Apply Security-Focused Instructions
Make secure coding part of the review prompt itself: request analysis for OWASP risks, SQL injection, XSS, data leaks, auth logic, or dependency vulnerabilities. Security is strongest when explicitly required.
Ask for Concrete Fixes, Not Just Criticism
Good feedback isn’t just “what’s wrong” — but how to improve it. Instruct AI to:
- rewrite unsafe logic
- simplify nested conditions
- correct recursion
- improve readability
- restructure functions
Validate Suggestions Against Standards
Verify recommendations against your team’s rules:
- style guides
- naming rules
- security practices
- testing policies
- framework conventions
AI “best practices” must match yours, not the other way around.
Run AI Review Iteratively
Review > Improve > Review again. After making changes, Treat AI review like test cycles — not one-off checks. Run a second prompt to confirm that:
- issues are resolved
- complexity didn’t increase
- logic remains correct
- no new risks were introduced
Don’t Hide Messy Code
AI is most useful on difficult, legacy, or unclear logic. Use it where you:
- refactor
- onboard new teammates
- ship complex features
- rely on tricky computational flows
If the code isn’t perfect, that’s exactly when review matters most.
Maintain Confidentiality
Never feed sensitive code, credentials, or proprietary algorithms into public models without data-safety controls. Use anonymization, masking, or local/self-hosted models when needed.
Treat AI Findings as Guidance — Not Absolute Truth
AI can misunderstand intent or propose over-engineered solutions.
Use its insights as a second opinion and apply engineering judgment to decide what actually matters.
Conclusion: Your Best Prompts for Code in One Guide
AI code review isn’t just a productivity booster — it’s a strategic upgrade to how modern engineering teams build software. By combining strong prompts, contextual instructions, and disciplined human oversight, AI transforms reviews into a faster, deeper, and more consistent process that catches issues early, strengthens security, reduces technical debt, and elevates overall code quality. When used thoughtfully, it becomes a silent team member that never gets tired, never misses patterns, and constantly encourages cleaner architecture and smarter decisions.
The future of code review isn’t manual vs. AI — it’s the synergy of both. Teams that embrace this balance ship better code, iterate faster, and stay more confident in every release.

Need Help With A Project?
Drop us a line, let’s arrange a discussion